- Gas Detector
- Gas Monitors
- Gas Analyzer
- Fixed Data Logger Scanner
- Clean Room Monitoring Equipment
- Internet Of Things (IoT)
- Temperature Humidity Transmitter
- Digital Stroboscope Tachometer
- Vibration Monitoring Equipments
- Gas Detection System
- Process Control Instruments
- Data Loggers
- Portable Gas Detectors
- Process Indicators
- Gas Alarm
- Calibration Kit
- Data Converters
- IIoT Loggers-Gateways
- Temperature Transmitter
- Sensors
- Gas Leak Detector
- Universal Data Logger
- Gas Leak Alert
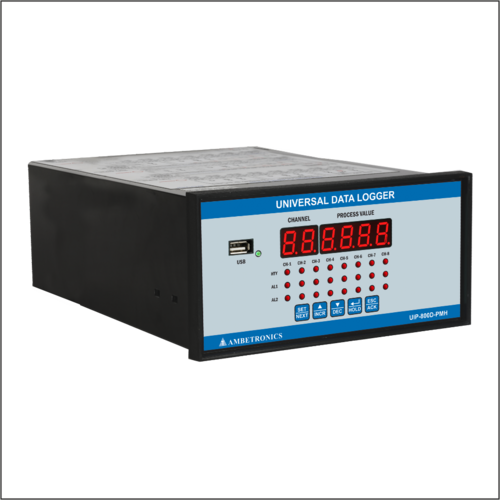

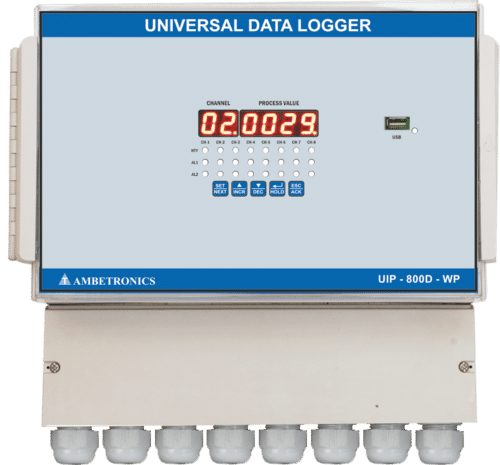
Universal Data Logger 1600D-PMH
29750 INR/Piece
Product Details:
- Material MS
- Alarm No
- Color White And Black
- Usage Industrial
- Display Type LED
- Click to view more
X
Universal Data Logger 1600D-PMH Price And Quantity
- 29750 INR/Piece
- 1 Piece
Universal Data Logger 1600D-PMH Product Specifications
- LED
- Industrial
- White And Black
- MS
- No
Universal Data Logger 1600D-PMH Trade Information
- 100 Piece Per Day
- 1 Week
- Africa Middle East Western Europe Eastern Europe Australia South America Central America Asia North America
- All India
- ISO 9001: 2015; CE Certification; CCOE & CMRI Approvals; PESO Tested.
Product Description
A Universal Data Logger 1600D-PMH is a device or software system used to record, store, and manage data from various sources and sensors. Its primary function is to collect data from different types of sensors and instruments, and then store, process, and present that data in a usable format. The data can be collected from a wide range of sources, such as temperature sensors, pressure sensors, flow meters, voltage/current sensors, environmental sensors, and many others.
Key features of a Universal Data Logger 1600D-PMH may include:
1. Multiple Input Support: The data logger can accept inputs from various sensors and data sources, regardless of the sensor type or measurement parameter.
2. Data Storage: It has the ability to store the collected data, either in local memory or external storage media like SD cards, USB drives, or cloud storage.
3. Data Visualization: The data logger may include built-in display options or the capability to connect to external devices like computers or smartphones to visualize the collected data in real-time or historical formats.
4. Data Processing: It can perform basic data processing tasks like averaging, scaling, filtering, and more to make the data more meaningful and useful.
5. Connectivity: Some universal data loggers offer options for connecting to different communication protocols, such as USB, Ethernet, Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, etc., to transfer data to other devices or systems.
6. Alarms and Notifications: The data logger might have the ability to set up alarms based on specific data thresholds or conditions, notifying users when certain criteria are met.
7. Compatibility: Universal data loggers are designed to work with a wide range of sensors, making them versatile and adaptable to various applications.
Applications of Universal Data Loggers include:
1. Environmental Monitoring: Collecting data on temperature, humidity, air quality, and other environmental parameters.
2. Industrial Process Monitoring: Monitoring and logging data from sensors in manufacturing processes to ensure quality and efficiency.
3. Agriculture: Monitoring soil moisture, temperature, and other agricultural parameters to optimize crop yield and resource usage.
4. Energy Management: Recording energy consumption data for buildings or industrial facilities to improve energy efficiency.
5. Research and Scientific Studies: Recording data in research experiments and studies to analyze and draw conclusions.
6. Weather Stations: Gathering weather data such as temperature, rainfall, wind speed, etc.
Tell us about your requirement

Price:
Quantity
Select Unit
- 50
- 100
- 200
- 250
- 500
- 1000+
Additional detail
Mobile number
Email
Other Products in 'Universal Data Logger' category
 |
AMBETRONICS ENGINEERS PVT. LTD.
All Rights Reserved.(Terms of Use) Developed and Managed by Infocom Network Private Limited. |

 English
English Spanish
Spanish French
French German
German Italian
Italian Chinese (Simplified)
Chinese (Simplified) Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Arabic
Arabic Portuguese
Portuguese